Understanding the results of your lung function tests is essential for managing your respiratory health effectively. When your healthcare provider reviews your test results, they may identify specific abnormalities that indicate how well your lungs function. Let’s explore common abnormalities in lung function tests and what they could mean for you:
Types of Abnormal Lung Function Patterns
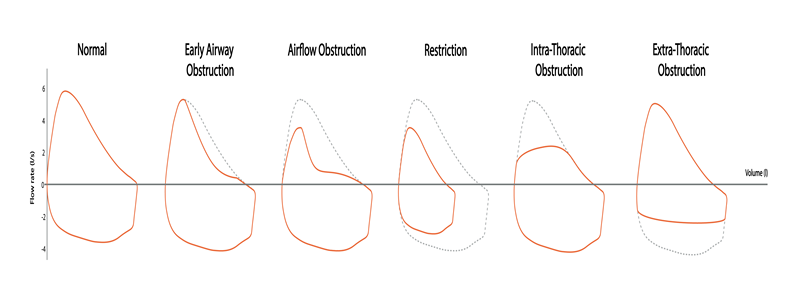
- Obstructive Lung Disease:
- Common Conditions: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma.
- Characteristics: Obstructive patterns show difficulty exhaling air from the lungs due to narrowed airways or blockages.
- Test Results: Lowered values in parameters like Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1) and FEV1/FVC ratio indicate obstructive lung disease.
- Restrictive Lung Disease:
- Common Conditions: Interstitial lung diseases, sarcoidosis.
- Characteristics: Restrictive patterns indicate reduced lung volume or capacity to expand.
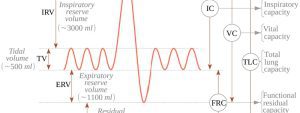
- Test Results: Decreased total lung capacity (TLC) and vital capacity (VC) are typical findings in restrictive lung diseases.
Understanding Specific Test Results
- FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second) Measures the air you can forcibly exhale in one second. Lower-than-average values may suggest obstructive lung disease.
- FVC (Forced Vital Capacity): Measures the total air you can exhale after a deep breath. Reduced FVC indicates restrictive lung disease.
- FEV1/FVC Ratio: Calculates the proportion of your lung capacity expelled in the first second of the forced breath. A lower ratio often points to obstructive lung diseases.
Implications of Abnormal Results
- Progression Monitoring: Abnormal lung function results help track disease progression, guiding treatment adjustments and interventions.
- Treatment Planning: Tailored treatments, such as bronchodilators for obstructive diseases or anti-inflammatory medications for restrictive diseases, aim to improve lung function and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Quitting smoking, avoiding pollutants, and incorporating exercise can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Discussing Results with Your Healthcare Provider
If you receive abnormal lung function results, discussing them promptly with your healthcare provider is essential. They can explain the findings for your health, recommend further tests or treatments, and develop a personalised care plan to optimise your lung function and overall well-being.
Interpreting abnormal lung function results empowers you to manage your respiratory health proactively. By understanding these patterns and their implications, you can work with your healthcare team at Care Net Consultants to monitor your lung health effectively and make informed decisions about your care. If you have any questions or concerns about your lung function tests, please don’t hesitate to contact us.